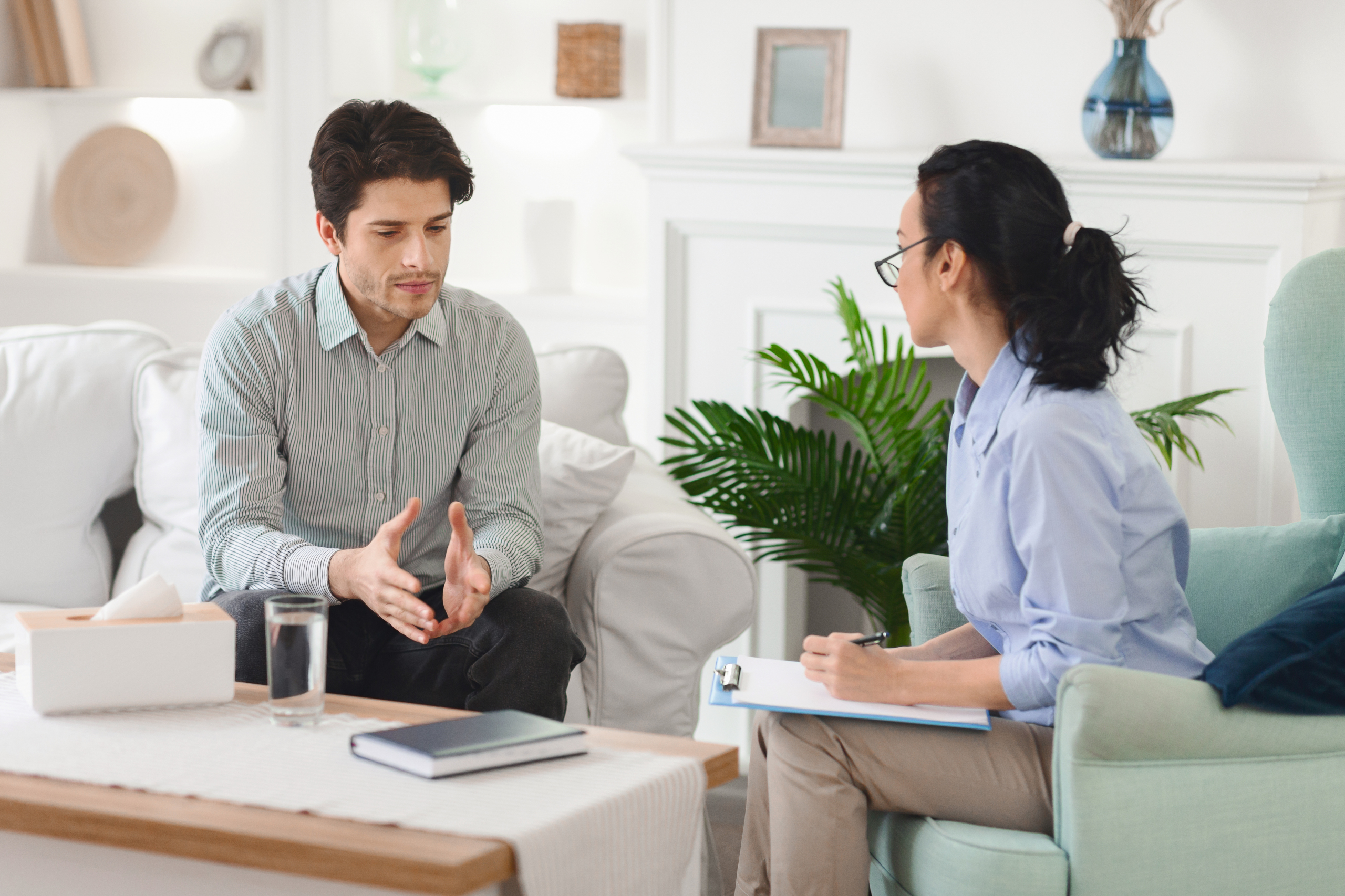
Talk therapy has been shown to be an extremely effective way for people to manage and overcome life’s more difficult periods. Whether you’re dealing with a chronic mental health challenge such as depression or anxiety, enduring a period of grief after a loss, or are going through something else entirely, there’s an undeniable power in the simple act of talking with someone whose job is to listen.
Of course, not all talk therapy works the same way. In fact, there are a number of different modalities and disciplines practiced around the world. The two most popular options in Ontario are Dialectical Behavioural Therapy (DBT) and Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT). However, you may be wondering, “DBT or CBT? Which one is right for me?” That’s why in this guide, we’ll explain each evidence-based talk therapy’s similarities, differences, and whether one might be a more suitable option than the other.
What is Dialectical Behavioural Therapy (DBT)?
DBT is a form of evidence-based talk therapy. Dialectical means ‘the existence of opposites’, which is a central part of this type of therapy. In practice, this means that DBT will often ask you to consider two seemingly opposite feelings, such as learning to be accepting of your current situation while also being willing to change it.
There are 4 cores in DBT, namely, emotion regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness. DBT helps clients to build a more holistic understanding of their issues and develops effective coping strategies based on the cores.
A Note on DBT-Informed Therapy
DBT is sometimes also used as a method of approaching more generalized talk therapy. Rather than focusing on the strict definition of the DBT process, DBT-informed therapy uses the principles and techniques of this system to guide therapy in a more general sense. Some practitioners find this to be a more customizable approach that works better for their patients. While DBT and DBT-informed therapy naturally share much in common, they are different processes.
Who Can DBT Help?
DBT was originally designed for people with borderline personality disorders. Today, we now know that it can be an invaluable tool to support people with other mental health challenges, including:
- Depression
- Self-harm tendencies
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Substance abuse and addiction
- Eating disorders
What is Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)?
CBT is another type of evidence-based therapy that aims to help shift negative thinking patterns in order to adjust your behaviour and emotions. CBT is based on three main principles:
- Psychological challenges stem from flawed, negative, or otherwise unhelpful thought patterns—at least in part.
- Psychological problems are also partly based on unhelpful, negative, and learned behaviour patterns.
- With time and effort, people dealing with psychological issues can learn to better cope with them, giving them relief from their symptoms and improving their lives.
Who Can CBT Help?
CBT offers a very useful set of emotional tools for anyone who’s going through a difficult time. It’s been shown to be particularly effective for those facing certain mental health struggles, including:
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Eating disorders
- Substance abuse
- Relationship challenges
- Severe episodes of mental disorders
What’s the Key Difference Between CBT and DBT?
With an understanding of these two types of therapy in their own right, we can break down the key difference between them.
While the process of CBT tends to look quite different from DBT, the major difference is the emphasis on relationships as part of the therapeutic process.
Generally speaking, CBT tends to be a more personal, inward process. It teaches you to change your negative thoughts and behaviours through the development of personal skills. In turn, this will help you control your emotions and mental symptoms.
DBT, on the other hand, places a special emphasis on relationships and interpersonal skills. DBT treatment often includes regular check-ins regarding successes and challenges in your interpersonal life. DBT practitioners might also work with you as you develop valuable relationship skills. DBT also teaches us to first learn to accept our thoughts and emotions, only then moving onto strategies to control, manage, and change them.
Get Started with Talk Therapy That Works for You
While the differences between CBT and DBT may seem subtle, anyone who has tried both can tell you that the processes feel very different as you’re going through them. There’s no way to know for certain which form of psychotherapy will be most beneficial for you without being assessed by a professional—an essential first step toward getting the support you need.
If you’d like to sit down with a trusted mental health professional to discuss what you’ve been feeling, thinking, and experiencing lately, we’re here to help. Our assessments are a great way to get objective about your mental health, as well as to lay the groundwork for a plan for ongoing treatment and support.
Contact us today to learn more about the different types of therapy and to find out which one might work for you. If you have any further questions that were not answered in our article or on our website, and you would like to speak to one of our staff directly about DBT or CBT, you can book a free 30-minute consultation by clicking here.








 by
by